| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
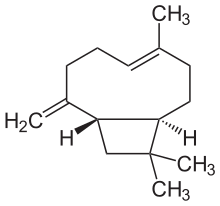
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,4E,9S)-4,11,11-Trimethyl-8-methylidenebicyclo[7.2.0]undec-4-ene | |
| Other names
β-Caryophyllene
trans-(1R,9S)-8-Methylene-4,11,11-trimethylbicyclo[7.2.0]undec-4-ene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.588 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.9052 g/cm3 (17 °C)[1] |
| Boiling point | 262–264 °C (504–507 °F; 535–537 K)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Caryophyllene (/ˌkærioʊˈfɪliːn/), more formally (−)-β-caryophyllene (BCP), is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that occurs widely in nature. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a trans-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both rarities in nature. [3]
- ^ SciFinder Record, CAS Registry Number 87-44-5
- ^ Baker, R. R. (2004). "The pyrolysis of tobacco ingredients". Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis. 71 (1): 223–311. doi:10.1016/s0165-2370(03)00090-1.
- ^ Sell, Charles S. (2006). "Terpenoids". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.2005181602120504.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.