| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
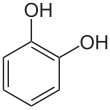
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene-1,2-diol[1] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 471401 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.025 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2936 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 110.112 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white to brown feathery crystals | ||
| Odor | faint, phenolic odor | ||
| Density | 1.344 g/cm3, solid | ||
| Melting point | 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 245.5 °C (473.9 °F; 518.6 K) (sublimes) | ||
| 312 g/L at 20 °C[2] | |||
| Solubility | very soluble in pyridine soluble in chloroform, benzene, CCl4, ether, ethyl acetate | ||
| log P | 0.88 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 20 Pa (20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.45, 12.8 | ||
| −6.876×10−5 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.604 | ||
| 2.62±0.03 D [3] | |||
| Structure | |||
| monoclinic | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−354.1 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Enthalpy of fusion (ΔfH⦵fus)
|
22.8 kJ·mol−1 (at melting point) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H311, H315, H317, H318, H332, H341 | |||
| P261, P301, P302, P305, P310, P312, P330, P331, P338, P351, P352 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 127 °C (261 °F; 400 K) | ||
| 510 °C (950 °F; 783 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.4%–?[4] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
300 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[4] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 5 ppm (20 mg/m3) [skin][4] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[4] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Sigma-Aldrich | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related benzenediols
|
Resorcinol Hydroquinone | ||
Related compounds
|
1,2-benzoquinone | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Catechol (/ˈkætɪtʃɒl/ or /ˈkætɪkɒl/), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H4(OH)2. It is the ortho isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Small amounts of catechol occur in fruits and vegetables.[2]
- ^ a b "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 691. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Ullmannwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lander, John J.; Svirbely, W. J. (1945). "The Dipole Moments of Catechol, Resorcinol and Hydroquinone". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 67 (2): 322–324. doi:10.1021/ja01218a051.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0109". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).