| Cephalosporin | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
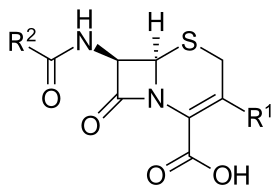 Core structure of the cephalosporins | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Use | Bacterial infection |
| ATC code | J01D |
| Biological target | Penicillin binding proteins |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | Drug Classes |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D002511 |
| Legal status | |
| In Wikidata | |
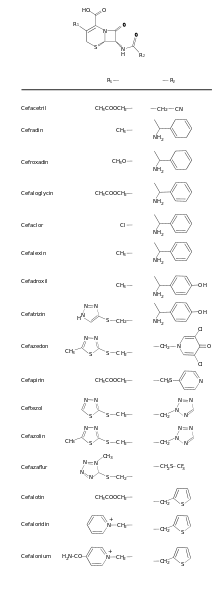
The cephalosporins (sg. /ˌsɛfələˈspɔːrɪn, ˌkɛ-, -loʊ-/[1][2]) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as Cephalosporium.[3]
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964.[4]
- ^ "cephalosporin". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ "cephalosporin – definition of cephalosporin in English from the Oxford dictionary". OxfordDictionaries.com. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ^ "cephalosporin" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology. OUP Oxford. 2009. p. 56. ISBN 9780191039621.