| Cervical vertebrae | |
|---|---|
 | |
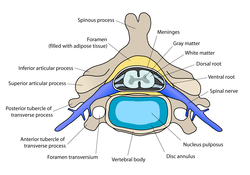 A human cervical vertebra | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vertebrae cervicales |
| MeSH | D002574 |
| TA98 | A02.2.02.001 |
| TA2 | 1032 |
| FMA | 9915 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (sg.: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae.[1] In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes.[citation needed] Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine.[2][3]
In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, and inferior cervical ganglion pass. The remainder of this article focuses upon human anatomy.
- ^ Schilling, N (10 February 2011). "Evolution of the axial system in craniates: morphology and function of the perivertebral musculature". Frontiers in Zoology. 8 (4): 3–4. doi:10.1186/1742-9994-8-4. PMC 3041741. PMID 21306656.
- ^ Varela-Lasheras, Irma; Bakker, Alexander J; Van Der Mije, Steven D; Metz, Johan AJ; Van Alphen, Joris; Galis, Frietson (2011). "Breaking evolutionary and pleiotropic constraints in mammals: On sloths, manatees and homeotic mutations". EvoDevo. 2: 11. doi:10.1186/2041-9139-2-11. PMC 3120709. PMID 21548920.
- "Sticking their necks out for evolution: Why sloths and manatees have unusually long (or short) necks". ScienceDaily (Press release). May 6, 2011.
- ^ Galis, Frietson (1999). "Why do almost all mammals have seven cervical vertebrae? Developmental constraints, Hox genes, and cancer". J. Exp. Zool. 285 (1): 19–26. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19990415)285:1<19::AID-JEZ3>3.0.CO;2-Z. PMID 10327647.