| Chemostat | |
|---|---|
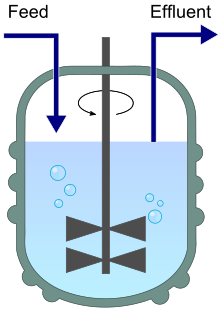 A chemostat diagram featuring inflow (feed) and outflow (effluent). | |
| Industry | Biological engineering |
| Application | Research and Industry |

A chemostat (from chemical environment is static) is a bioreactor to which fresh medium is continuously added, while culture liquid containing left over nutrients, metabolic end products and microorganisms is continuously removed at the same rate to keep the culture volume constant.[2][3] By changing the rate with which medium is added to the bioreactor the specific growth rate of the microorganism can be easily controlled within limits.
- ^ Madigan, Michael (2015). Brock Biology of Microorganisms. Pearson. pp. 152–153. ISBN 978-0-321-89739-8.
- ^ Novick A, Szilard L (1950). "Description of the Chemostat". Science. 112 (2920): 715–6. Bibcode:1950Sci...112..715N. doi:10.1126/science.112.2920.715. PMID 14787503.
- ^ James TW (1961). "Continuous Culture of Microorganisms". Annual Review of Microbiology. 15: 27–46. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.15.100161.000331.