| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
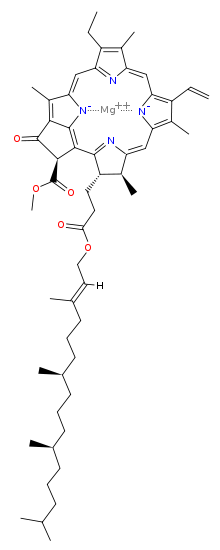
| IUPAC name
Chlorophyll a
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Magnesium [methyl (3S,4S,21R)-14-ethyl-4,8,13,18-tetramethyl-20-oxo-3-(3-oxo-3-{[(2E,7R,11R)-3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecen-1-yl]oxy}propyl)-9-vinyl-21-phorbinecarboxylatato(2−)-κ2N,N′] | |
| Other names
α-Chlorophyll
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.852 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C55H72MgN4O5 | |
| Molar mass | 893.509 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Green |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.079 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | ~ 152.3 °C (306.1 °F; 425.4 K)[2] decomposes[1] |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Very soluble in ethanol, ether Soluble in ligroin,[2] acetone, benzene, chloroform[1] |
| Absorbance | See text |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chlorophyll a is a specific form of chlorophyll used in oxygenic photosynthesis. It absorbs most energy from wavelengths of violet-blue and orange-red light, and it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum.[3] Chlorophyll does not reflect light but chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light is diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls.[4] This photosynthetic pigment is essential for photosynthesis in eukaryotes, cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes because of its role as primary electron donor in the electron transport chain.[5] Chlorophyll a also transfers resonance energy in the antenna complex, ending in the reaction center where specific chlorophylls P680 and P700 are located.[6]
- ^ a b c Anatolievich KR. "Chlorophyll a". chemister.ru. Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 2014-08-23.
- ^ a b Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ "Photosynthesis". Archived from the original on 2009-11-28.
- ^ Virtanen O, Constantinidou E, Tyystjärvi E (December 2020). "Chlorophyll does not reflect green light - how to correct a misconception". Journal of Biological Education. 56 (5): 552–559. doi:10.1080/00219266.2020.1858930.
- ^ Raven PH, Evert RF, Eichhorn SE (2005). "Photosynthesis, Light, and Life". Biology of Plants (7th ed.). W. H. Freeman. pp. 119–127. ISBN 0-7167-9811-5.
- ^ Papageorgiou G, Govindjee (2004). Chlorophyll a Fluorescence, A Signature of Photosynthesis. Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration. Vol. 19. Springer. pp. 14, 48, 86.