| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
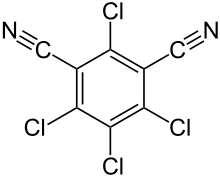
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,5,6-Tetrachlorobenzene-1,3-dicarbonitrile | |
| Other names
2,4,5,6-Tetrachloroisophthalonitrile
Bravo Daconil Tetrachloroisophthalonitrile Celeste Bronco Agronil Aminil | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.990 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3276, 2588 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8Cl4N2 | |
| Molar mass | 265.90 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.8 g cm−3, solid |
| Melting point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
| Boiling point | 350 °C (662 °F; 623 K) (760 mmHg) |
| 10 mg/100 mL[1] | |
| log P | 2.88–3.86 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| H317, H318, H330, H335, H351, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P284, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P312, P320, P321, P333+P313, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related nitriles; organochlorides
|
benzonitrile; hexachlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, chlorobenzene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chlorothalonil (2,4,5,6-tetrachloroisophthalonitrile) is an organic compound mainly used as a broad spectrum, nonsystemic fungicide, with other uses as a wood protectant, pesticide, acaricide, and to control mold, mildew, bacteria, algae.[2] Chlorothalonil-containing products are sold under the names Bravo, Echo, and Daconil. It was first registered for use in the US in 1966. In 1997, the most recent year for which data are available, it was the third most used fungicide in the US, behind only sulfur and copper, with 12 million pounds (5.4 million kilograms) used in agriculture that year.[3] Including nonagricultural uses, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates, on average, almost 15 million lb (6.8 million kg) were used annually from 1990 to 1996.[2]
- ^ "Chlorothalonil". Pubchem.
- ^ a b Reregistration Eligibility Decision for chlorothalonil, US EPA, 1999.
- ^ PESTICIDE USE IN U.S. CROP PRODUCTION: 1997 Archived 10 December 2006 at the Wayback Machine National Center for Food and Agricultural Policy, 1997.