| Cholescintigraphy | |
|---|---|
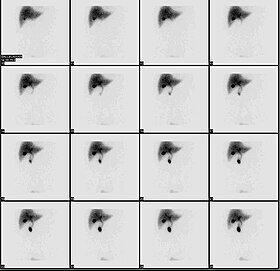 Normal hepatobiliary scan (HIDA scan). The nuclear medicine hepatobiliary scan is clinically useful in the detection of the gallbladder disease. | |
| ICD-9-CM | 92.02 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-707.6 |
Cholescintigraphy or hepatobiliary scintigraphy is scintigraphy of the hepatobiliary tract, including the gallbladder and bile ducts. The image produced by this type of medical imaging, called a cholescintigram, is also known by other names depending on which radiotracer is used, such as HIDA scan, PIPIDA scan, DISIDA scan, or BrIDA scan.[1][2] Cholescintigraphic scanning is a nuclear medicine procedure to evaluate the health and function of the gallbladder and biliary system. A radioactive tracer is injected through any accessible vein and then allowed to circulate to the liver, where it is excreted into the bile ducts and stored by the gallbladder[3] until released into the duodenum.
Use of cholescintigraphic scans as a first-line form of imaging varies depending on indication. For example for cholecystitis, cheaper and less invasive ultrasound imaging may be preferred,[4] while for bile reflux cholescintigraphy may be the first choice.[5]
- ^ Lambie, H.; Cook, A.M.; Scarsbrook, A.F.; Lodge, J.P.A.; Robinson, P.J.; Chowdhury, F.U. (November 2011). "Tc99m- hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scintigraphy in clinical practice". Clinical Radiology. 66 (11): 1094–1105. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2011.07.045. PMID 21861996.
- ^ Kim, Chun K; Joo, Junghyun; Lee, Seokmo (2015). "Digestive System 2: Liver and Biliary Tract". In Elgazzar, Abedlhamid H (ed.). The pathophysiologic basis of nuclear medicine (3rd ed.). Cham: Springer. p. 561. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-06112-2. ISBN 9783319061115.
- ^ Michael, Picco, M.D. "HIDA scan (cholescintigraphy): Why is it performed?". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2007-12-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kelly, Aine; Cronin, Paul; Puig, Stefan; Applegate, Kimberly E. (2018). Evidence-Based Emergency Imaging: Optimizing Diagnostic Imaging of Patients in the Emergency Care Setting. Springer. p. 313. ISBN 978-3-319-67066-9.
- ^ Eldredge, Thomas A.; Myers, Jennifer C.; Kiroff, George K.; Shenfine, Jonathan (11 December 2017). "Detecting Bile Reflux—the Enigma of Bariatric Surgery". Obesity Surgery. 28 (2): 559–566. doi:10.1007/s11695-017-3026-6. PMID 29230622. S2CID 6118821.