| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium[1]
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethan-1-aminium | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1736748 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.487 |
| EC Number |
|
| 324597 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
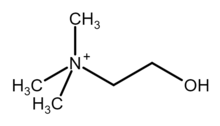
| [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+ | |
| Molar mass | 104.173 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Viscous colorless deliquescent liquid (choline hydroxide)[2] |
| Very soluble (choline hydroxide)[2] | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol,[2] insoluble in diethylether and chloroform[3] (choline hydroxide) |
| Structure | |
| Tetrahedral at the nitrogen atom | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
3–6 g/kg (rat, oral)[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | 4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Choline is a cation with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+.[1][4][5] Choline forms various salts, such as choline chloride and choline bitartrate. It is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals, and is a structural part of phospholipids and cell membranes.[4][5]
Choline is used to synthesize acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in muscle control and numerous functions of the nervous system.[4][5] Choline is involved in early development of the brain, gene expression, cell membrane signaling, and brain metabolism.[5]
Although humans synthesize choline in the liver, the amount produced naturally is insufficient to meet cellular functions, requiring that some choline be obtained from foods or dietary supplements.[5] Foods rich in choline include meats, poultry, eggs, and other animal-based products, cruciferous vegetables, beans, nuts, and whole grains.[5] Choline is present in breast milk and is commonly added as an ingredient to baby foods.[5]
- ^ a b "Choline". PubChem, National Library of Medicine, US National Institutes of Health. 26 October 2024. Retrieved 31 October 2024.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Kirk 2000was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
zewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c "Choline". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis. July 2023. Retrieved 31 October 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Choline". Office of Dietary Supplements, US National Institutes of Health. 2 June 2022. Retrieved 31 October 2024.
