| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
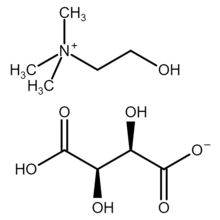
| IUPAC name
Choline (2R,3R)-bitartrate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2-Hydroxyethyl)trimethylaminium hydrogen (2R,3R)-tartrate[2] | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.604 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H19NO7 | |
| Molar mass | 253.251 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder[1][2] |
| Odor | Odorless or faint trimethylamine-like odor[1] |
| Melting point | 147–153 °C (297–307 °F; 420–426 K)[1][2] |
| Solubility | Water (slightly), ethanol (slightly), DMSO (slightly), methanol (slightly, when heated); insoluble in diethyl ether, chloroform and benzene[1][2] |
| Structure | |
| Tetrahedral molecular geometry at the nitrogen atom | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
200 to 400 grams (as choline, human, estimated)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
|
Other cations
|
N,N-Dimethylethanolamine bitartrate |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Choline bitartrate is an organic compound with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+HOOC−CH(OH)−CH(OH)−COO−. It is a white crystalline powder with an acid taste.[1] It is hygroscopic when exposed to air.[1] Modern texts refer to the choline salt of the natural form of tartaric acid, that is, the salt called choline dextrobitartrate, choline (2R,3R)-bitartrate or choline L-(+)-bitartrate.