 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.608 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
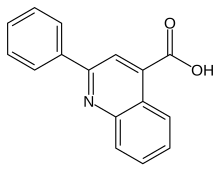
| Formula | C16H11NO2 |
| Molar mass | 249.269 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cinchophen (trade names Atophan, Quinophan, and Phenaquin) is an analgesic drug that was first produced by Doebner & Gieskel in 1887, it was commercially introduced in 1908 as a treatment for gout. This drug is still used, in combination with Prednisolone, by veterinarians to treat arthritis in animals. It can be prepared starting from anilin, benzaldehyde and pyruvic acid in absolute ethanol.[1] Use of this drug in humans ceased in the 1930s due to the discovery that cinchophen can cause serious liver damage.[2] There is some evidence that it stimulates C-Fos.[3]
- ^ Ahluwalia VK (2005). Intermediates for Organic Synthesis. I. K. International. p. 262. ISBN 978-81-88-237-33-3.
- ^ Cutrín Prieto C, Nieto Pol E, Batalla Eiras A, Casal Iglesias L, Pérez Becerra E, Lorenzo Zúñiga V (June 1991). "[Toxic hepatitis from cinchophen: report of 3 cases]". Medicina Clinica (in Spanish). 97 (3): 104–106. PMID 1679861.
- ^ Takayama K, Xiong Y, Miura M (May 1994). "Neuronal expression of Fos protein in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus after i.p. injection of ulcergenic cinchophen". Neuroscience Letters. 172 (1–2): 55–58. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(94)90661-0. PMID 7916144. S2CID 22824054.