 A two-pole miniature circuit breaker | |
| Electronic symbol | |
|---|---|
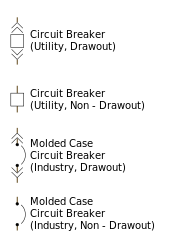 |


| Electrical installations |
|---|
| Wiring practice by region or country |
| Regulation of electrical installations |
| Cabling and accessories |
| Switching and protection devices |
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by current in excess of that which the equipment can safely carry (overcurrent). Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation.
Circuit breakers are commonly installed in distribution boards. Apart from its safety purpose, a circuit breaker is also often used as a main switch to manually disconnect ("rack out") and connect ("rack in") electrical power to a whole electrical sub-network.[1]
Circuit breakers are made in varying current ratings, from devices that protect low-current circuits or individual household appliances, to switchgear designed to protect high-voltage circuits feeding an entire city. Any device which protects against excessive current by automatically removing power from a faulty system, such as a circuit breaker or fuse, can be referred to as an over-current protection device (OCPD).
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions at the Safe-T-Rack company website. Accessed on 2024-07-28.