| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Citric acid[1]
| |||
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.973 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E330 (antioxidants, ...) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H8O7 | |||
| Molar mass | 192.123 g/mol (anhydrous), 210.14 g/mol (monohydrate)[2] | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 1.665 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.542 g/cm3 (18 °C, monohydrate) | ||
| Melting point | 156 °C (313 °F; 429 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K) decomposes from 175 °C[3] | ||
| 54% w/w (10 °C) 59.2% w/w (20 °C) 64.3% w/w (30 °C) 68.6% w/w (40 °C) 70.9% w/w (50 °C) 73.5% w/w (60 °C) 76.2% w/w (70 °C) 78.8% w/w (80 °C) 81.4% w/w (90 °C) 84% w/w (100 °C)[4] | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, alcohol, ether, ethyl acetate, DMSO Insoluble in C 6H 6, CHCl3, CS2, toluene[3] | ||
| Solubility in ethanol | 62 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| Solubility in amyl acetate | 4.41 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | 1.05 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| Solubility in 1,4-dioxane | 35.9 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| log P | −1.64 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = 3.13[5] pKa2 = 4.76[5] pKa3 = 6.39,[6] 6.40[7] pKa4 = 14.4[8] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.493–1.509 (20 °C)[4] 1.46 (150 °C)[3] | ||
| Viscosity | 6.5 cP (50% aq. sol.)[4] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Monoclinic | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
226.51 J/(mol·K) (26.85 °C)[9] | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
252.1 J/(mol·K)[9] | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1543.8 kJ/mol[4] | ||
| 1985.3 kJ/mol (474.5 kcal/mol, 2.47 kcal/g),[4] 1960.6 kJ/mol[9] 1972.34 kJ/mol (471.4 kcal/mol, 2.24 kcal/g) (monohydrate)[4] | |||
| Pharmacology | |||
| A09AB04 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Skin and eye irritant | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  [5] [5]
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H290, H319, H315[5] | |||
| P305+P351+P338[5] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) | ||
| 345 °C (653 °F; 618 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 8%[5] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
3000 mg/kg (rats, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | HMDB (PDF) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
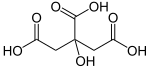
Citric acid is an organic compound with the skeletal formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2.[10] It is a colorless weak organic acid.[10] It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.[10]
More than two million tons of citric acid are manufactured every year. It is used widely as acidifier, flavoring, preservative, and chelating agent.[11]
A citrate is a derivative of citric acid; that is, the salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion found in solutions and salts of citric acid. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate. When citrate trianion is part of a salt, the formula of the citrate trianion is written as C
6H
5O3−
7 or C
3H
5O(COO)3−
3.
- ^ a b International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 747. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ CID 22230 from PubChem
- ^ a b c d e f g "citric acid". chemister.ru. Archived from the original on November 29, 2014. Retrieved June 1, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f CID 311 from PubChem
- ^ a b c d e f Fisher Scientific, Citric acid. Retrieved on 2014-06-02.
- ^ "Data for Biochemical Research". ZirChrom Separations, Inc. Retrieved January 11, 2012.
- ^ "Ionization Constants of Organic Acids". Michigan State University. Retrieved January 11, 2012.
- ^ Silva, Andre M. N.; Kong, Xiaole; Hider, Robert C. (2009). "Determination of the pKa value of the hydroxyl group in the α-hydroxycarboxylates citrate, malate and lactate by 13C NMR: implications for metal coordination in biological systems". BioMetals. 22 (5): 771–778. doi:10.1007/s10534-009-9224-5. ISSN 0966-0844. PMID 19288211.
- ^ a b c Citric acid in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD) (retrieved 2014-06-02)
- ^ a b c "Citric acid | C6H8O7 - PubChem". Archived from the original on January 19, 2022. Retrieved December 19, 2021.
- ^ Apleblat, Alexander (2014). Citric acid. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-11232-9.