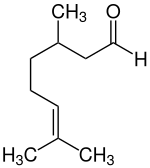
| |
 (+)-Citronellal
| |
 (-)-Citronellal
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,7-dimethyloct-6-enal
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1209447 1720789 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.070 |
| EC Number |
|
| 1521962 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H18O | |
| Molar mass | 154.25 g/mol |
| Density | 0.855 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 201 to 207 °C (394 to 405 °F; 474 to 480 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  [2] [2]
| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H317, H411[2] | |
| P262, P273, P280, P302+P352[2] | |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkenals
|
Citral |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Citronellal or rhodinal (C10H18O) is a monoterpenoid aldehyde, the main component in the mixture of terpenoid chemical compounds that give citronella oil its distinctive lemon scent.
Citronellal is a main isolate in distilled oils from the plants Cymbopogon (excepting C. citratus, culinary lemongrass),[3] lemon-scented gum, and lemon-scented teatree. The (S)-(−)-enantiomer of citronellal makes up to 80% of the oil from kaffir lime leaves and is the compound responsible for its characteristic aroma.
Citronellal has insect repellent properties, and research shows high repellent effectiveness against mosquitoes.[4] Another research shows that citronellal has strong antifungal qualities.[5]
- ^ Citronellal, The Merck Index, 12th Edition
- ^ a b c Record of Citronellal in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 13 March 2020.
- ^ Mahalwal, Vijender S.; Ali, Mohd. (2003). "Volatile constituents of Cymbopogon nardus (Linn.) Rendle". Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 18: 73–76. doi:10.1002/ffj.1144.
- ^ Jeong-Kyu KIM; Chang-Soo KANG; Jong-Kwon LEE; Young-Ran KIM; Hye-Yun HAN; Hwa Kyung YUN (2005). "Evaluation of Repellency Effect of Two Natural Aroma Mosquito Repellent Compounds, Citronella and Citronellal". Entomological Research. 35 (2): 117–120. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5967.2005.tb00146.x. S2CID 85112045.
- ^ Kazuhiko NAKAHARA, Najeeb S. ALZOREKY1, Tadashi YOSHIHASHI, Huong T. T. NGUYEN and Gassinee TRAKOONTIVAKORN (2003). "Chemical Composition and Antifungal Activity of Essential Oil from Cymbopogon nardus (Citronella Grass)". JARQ. 37 (4).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)