| Cladosporium cladosporioides | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Dothideomycetes |
| Order: | Capnodiales |
| Family: | Davidiellaceae |
| Genus: | Cladosporium |
| Species: | C. cladosporioides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cladosporium cladosporioides (Fresen.) G.A.de Vries (1952)
| |
| Synonyms | |
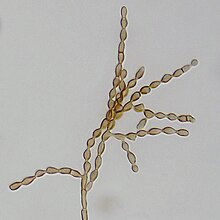
Cladosporium cladosporioides is a darkly pigmented mold that occurs world-wide on a wide range of materials both outdoors and indoors.
It is known for its role in the decomposition of organic matter and its presence in indoor and outdoor environments. This species is also notable for its potential impact on human health, particularly in individuals with respiratory conditions.[1]
It is one of the most common fungi in outdoor air where its spores are important in seasonal allergic disease. While this species rarely causes invasive disease in animals, it is an important agent of plant disease, attacking both the leaves and fruits of many plants. This species produces asexual spores in delicate, branched chains that break apart readily and drift in the air. It is able to grow under low water conditions and at very low temperatures.
- ^ Bensch, K.; Braun, U.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. (June 2012). "The genus Cladosporium". Studies in Mycology. 72: 1–401. doi:10.3114/sim0003. ISSN 0166-0616.