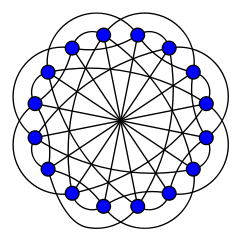
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Clebsch graph is either of two complementary graphs on 16 vertices, a 5-regular graph with 40 edges and a 10-regular graph with 80 edges. The 80-edge graph is the dimension-5 halved cube graph; it was called the Clebsch graph name by Seidel (1968)[2] because of its relation to the configuration of 16 lines on the quartic surface discovered in 1868 by the German mathematician Alfred Clebsch. The 40-edge variant is the dimension-5 folded cube graph; it is also known as the Greenwood–Gleason graph after the work of Robert E. Greenwood and Andrew M. Gleason (1955), who used it to evaluate the Ramsey number R(3,3,3) = 17.[3][4][5]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
MathWorldwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ J. J. Seidel, Strongly regular graphs with (−1,1,0) adjacency matrix having eigenvalue 3, Lin. Alg. Appl. 1 (1968) 281-298.
- ^ Clebsch, A. (1868), "Ueber die Flächen vierter Ordnung, welche eine Doppelcurve zweiten Grades besitzen", Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik, 69: 142–184.
- ^ "The Clebsch Graph on Bill Cherowitzo's home page" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-29. Retrieved 2011-05-21.
- ^ Greenwood, R. E.; Gleason, A. M. (1955), "Combinatorial relations and chromatic graphs", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 7: 1–7, doi:10.4153/CJM-1955-001-4, MR 0067467.