 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682542 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 39.2% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 21.3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
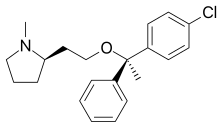
| Formula | C21H26ClNO |
| Molar mass | 343.90 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Clemastine, also known as meclastin, is a first-generation H1 histamine antagonist (antihistamine) with anticholinergic properties (drying) and sedative side effects.[1] Like all first-generation antihistamines, it is sedating.[2][3]
Patented in 1960, it came into medical use in 1967.[4]
- ^ "Clemastine". DrugBank.com.
- ^ "Perspectives on Second-Generation OTC Antihistamines". Pharmacy Times. 2012-03-30. Archived from the original on 2012-05-01.
- ^ Krouse JH (April 2008). "Allergic rhinitis--current pharmacotherapy". Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. 41 (2): 347–58, vii. doi:10.1016/j.otc.2007.11.014. PMID 18328373.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 547. ISBN 9783527607495.