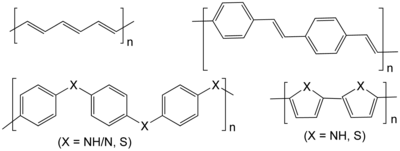
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity.[1][2] Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The main advantage of conductive polymers is that they are easy to process, mainly by dispersion. Conductive polymers are generally not thermoplastics, i.e., they are not thermoformable. But, like insulating polymers, they are organic materials. They can offer high electrical conductivity but do not show similar mechanical properties to other commercially available polymers. The electrical properties can be fine-tuned using the methods of organic synthesis[3] and by advanced dispersion techniques.[4]
- ^ Inzelt, György (2008). "Chapter 1: Introduction". In Scholz, F. (ed.). Conducting Polymers: A New Era in Electrochemistry. Monographs in Electrochemistry. Springer. pp. 1–6. ISBN 978-3-540-75929-4.
- ^ Conducting Polymers, Editor: Toribio Fernandez Otero, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge 2016, https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/ebook/978-1-78262-374-8
- ^ Naarmann, Herbert (2000). "Polymers, Electrically Conducting". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_429. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
nalwawas invoked but never defined (see the help page).