| Congenital hypothyroidism | |
|---|---|
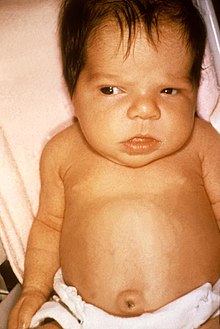 | |
| 6 week old female with jaundice due to hypothyroidism. | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth. If untreated for several months after birth, severe congenital hypothyroidism can lead to growth failure and permanent intellectual disability. Infants born with congenital hypothyroidism may show no effects, or may display mild effects that often go unrecognized as a problem. Significant deficiency may cause excessive sleeping, reduced interest in nursing, poor muscle tone, low or hoarse cry, infrequent bowel movements, significant jaundice, and low body temperature.[citation needed]
Causes of congenital hypothyroidism include iodine deficiency and a developmental defect in the thyroid gland, either due to a genetic defect or of unknown cause.
Treatment consists of a daily dose of thyroid hormone (thyroxine) by mouth. Because the treatment is simple, effective, and inexpensive, most of the developed world utilizes newborn screening with blood thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels to detect congenital hypothyroidism. Most children with congenital hypothyroidism correctly treated with thyroxine grow and develop normally in all respects. Approximately 1 in 4000 newborns have a severe deficiency of thyroid function; a greater number have a mild or moderate deficiency.