| Connexin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
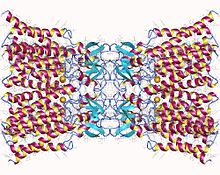 Connexin-26 dodecamer. A gap junction, composed of twelve identical connexin proteins, six in the membrane of each cell. Each of these six units is a single polypeptide which passes the membrane four times (referred to as four-pass transmembrane proteins). | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Connexin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00029 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013092 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00341 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.A.24 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 194 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 2zw3 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Connexins (Cx) (TC# 1.A.24), or gap junction proteins, are structurally related transmembrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions. An entirely different family of proteins, the innexins, forms gap junctions in invertebrates.[1] Each gap junction is composed of two hemichannels, or connexons, which consist of homo- or heterohexameric arrays of connexins, and the connexon in one plasma membrane docks end-to-end with a connexon in the membrane of a closely opposed cell. The hemichannel is made of six connexin subunits, each of which consist of four transmembrane segments. Gap junctions are essential for many physiological processes, such as the coordinated depolarization of cardiac muscle, proper embryonic development, and the conducted response in microvasculature. Connexins also have non-channel dependant functions relating to cytoskeleton and cell migration.[2] For these reasons, mutations in connexin-encoding genes can lead to functional and developmental abnormalities.
- ^ Lodish HF, Berk A, Matsudaira P, Kaiser CA, Krieger M, Scott MP, Zipursky SL, Darnell J (2004). Molecular Cell Biology (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. pp. 230–31. ISBN 0-7167-4366-3.
- ^ Matsuuchi L, Naus CC (January 2013). "Gap junction proteins on the move: connexins, the cytoskeleton and migration". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1828 (1): 94–108. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.05.014. PMID 22613178.