
| |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Copper(I) oxide
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.883 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cu2O | |
| Molar mass | 143.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | brownish-red solid |
| Density | 6.0 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,232 °C (2,250 °F; 1,505 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,800 °C (3,270 °F; 2,070 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility in acid | Soluble |
| Band gap | 2.137 eV |
| −20×10−6 cm3/mol | |
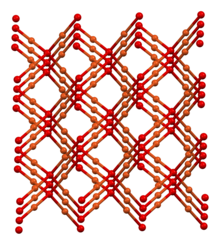
| Structure | |
| cubic | |
| Pn3m, #224 | |
a = 4.2696
| |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
93 J·mol−1·K−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−170 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H318, H332, H410 | |
| P273, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | SIRI.org |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Copper(I) sulfide Copper(II) sulfide Copper(I) selenide |
Other cations
|
Copper(II) oxide Silver(I) oxide Nickel(II) oxide Zinc oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Copper(I) oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O. It is one of the principal oxides of copper, the other being copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide (CuO).The compound can appear either yellow or red, depending on the size of the particles.[2] Cuprous oxide is found as the mineral cuprite. It is a component of some antifouling paints, but also has other applications including some that exploit its property as a semiconductor.
