| Nucleocapsid protein | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
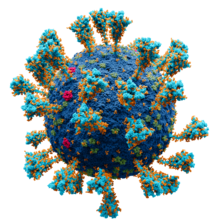 Model of the external structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virion.[1] The N protein, contained entirely within the virion, is not visible.
● Blue: envelope ● Turquoise: spike glycoprotein (S) ● Red: envelope proteins (E) ● Green: membrane proteins (M) ● Orange: glycans | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | CoV_nucleocap | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00937 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001218 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The nucleocapsid (N) protein is a protein that packages the positive-sense RNA genome of coronaviruses to form ribonucleoprotein structures enclosed within the viral capsid.[2][3] The N protein is the most highly expressed of the four major coronavirus structural proteins.[2] In addition to its interactions with RNA, N forms protein-protein interactions with the coronavirus membrane protein (M) during the process of viral assembly.[2][3] N also has additional functions in manipulating the cell cycle of the host cell.[3][4] The N protein is highly immunogenic and antibodies to N are found in patients recovered from SARS and COVID-19.[5]
- ^ Solodovnikov, Alexey; Arkhipova, Valeria (2021-07-29). "Достоверно красиво: как мы сделали 3D-модель SARS-CoV-2" [Truly beautiful: how we made the SARS-CoV-2 3D model] (in Russian). N+1. Archived from the original on 2021-07-30. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ a b c Chang, Chung-ke; Hou, Ming-Hon; Chang, Chi-Fon; Hsiao, Chwan-Deng; Huang, Tai-huang (March 2014). "The SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein – Forms and functions". Antiviral Research. 103: 39–50. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.12.009. PMC 7113676. PMID 24418573.
- ^ a b c McBride, Ruth; van Zyl, Marjorie; Fielding, Burtram (7 August 2014). "The Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Is a Multifunctional Protein". Viruses. 6 (8): 2991–3018. doi:10.3390/v6082991. PMC 4147684. PMID 25105276.
- ^ Su, Mingjun; Chen, Yaping; Qi, Shanshan; Shi, Da; Feng, Li; Sun, Dongbo (5 November 2020). "A Mini-Review on Cell Cycle Regulation of Coronavirus Infection". Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 7: 586826. doi:10.3389/fvets.2020.586826. PMC 7674852. PMID 33251267.
- ^ Li, Dandan; Li, Jinming (20 April 2021). "Immunologic Testing for SARS-CoV-2 Infection from the Antigen Perspective". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 59 (5): e02160-20. doi:10.1128/JCM.02160-20. PMC 8091849. PMID 33318065.