This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (June 2014) |
| Coxa vara | |
|---|---|
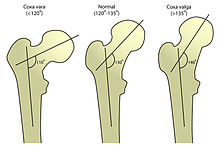 | |
| Left to right: coxa vara, normal femur, coxa valga | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Coxa vara is a deformity of the hip, whereby the angle between the head and the shaft of the femur is reduced to less than 120 degrees. This results in the leg being shortened and the development of a limp. It may be congenital and is commonly caused by injury, such as a fracture. It can also occur when the bone tissue in the neck of the femur is softer than normal, causing it to bend under the weight of the body. This may either be congenital or the result of a bone disorder. The most common cause of coxa vara is either congenital or developmental. Other common causes include metabolic bone diseases (e.g. Paget's disease of bone), post-Perthes deformity, osteomyelitis, and post traumatic (due to improper healing of a fracture between the greater and lesser trochanter). Shepherd's Crook deformity is a severe form of coxa vara where the proximal femur is severely deformed with a reduction in the neck shaft angle beyond 90 degrees. It is most commonly a sequela of osteogenesis imperfecta, Paget's disease, osteomyelitis, tumour and tumour-like conditions (e.g. fibrous dysplasia).
Coxa vara can happen in cleidocranial dysostosis.