This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
Crossover distortion is a type of distortion which is caused by switching between devices driving a load.[1] It is most commonly seen in complementary, or "push-pull", class-B amplifier stages, although it is occasionally seen in other types of circuits as well.
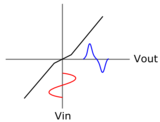
The term crossover signifies the "crossing over" of the signal between devices, in this case, from the upper transistor to the lower and vice versa. The term is not related to the audio loudspeaker crossover filter—a filtering circuit which divides an audio signal into frequency bands to drive separate drivers in multiway speakers.
- ^ "Preface to the Sixth Edition - Audio Power Amplifier Design, 6th Edition [Book]". www.oreilly.com. Retrieved 2022-12-04.