Cyme Κύμη | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8th century – 241 BC | |||||||||
Silver tetradrachm of Cyme, 165–140 BC
| |||||||||
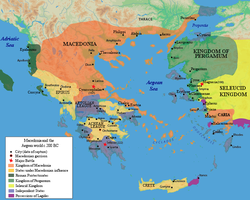 Map of Asia Minor showing the location of Kyme in the southwest coast of the Kingdom of Pergamum. | |||||||||
| Capital | Kymi | ||||||||
| Common languages | Aeolic, Ionic Greek | ||||||||
| Religion | Greek Polytheism | ||||||||
| Government | Tyranny | ||||||||
| Historical era | Classical Antiquity | ||||||||
• Established | 8th century | ||||||||
• Colony established | c. 700 – 600 BC | ||||||||
• Persian Conquest | 542 BC | ||||||||
| 499–493 BC | |||||||||
| 336–323 BC | |||||||||
| 241–133 BC | |||||||||
| 133 BC | |||||||||
• Disestablished | 241 BC | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Cyme (Greek: Κύμη) or Cumae was an Aeolian city in Aeolis (Asia Minor) close to the kingdom of Lydia. It was called Phriconian, perhaps from the mountain Phricion in Aeolis, near which the Aeolians had been settled before their migration to Asia.[1]
The Aeolians regarded Cyme as the largest and most important of their twelve cities, which were located on the coastline of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey).[citation needed] As a result of their direct access to the sea, unlike most non-landlocked settlements of the ancient world, trade is believed to have prospered.