 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌsaɪproʊˈhɛptədiːn/[1] |
| Trade names | Periactin, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682541 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 96 to 99% |
| Metabolism | Liver,[3][4] mostly CYP3A4 mediated. |
| Elimination half-life | 8.6 hours[2] |
| Excretion | Faecal (2–20%; of which, 34% as unchanged drug) and renal (40%; none as unchanged drug)[3][4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.482 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
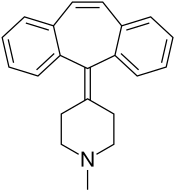
| Formula | C21H21N |
| Molar mass | 287.406 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cyproheptadine, sold under the brand name Periactin among others, is a first-generation antihistamine with additional anticholinergic, antiserotonergic, and local anesthetic properties.
It was patented in 1959 and came into medical use in 1961.[5] In 2021, it was the 280th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 800,000 prescriptions.[6][7]
- ^ "Cyproheptadine". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d.
- ^ Gunja N, Collins M, Graudins A (2004). "A comparison of the pharmacokinetics of oral and sublingual cyproheptadine". Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology. 42 (1): 79–83. doi:10.1081/clt-120028749. PMID 15083941. S2CID 20196551.
- ^ a b "Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride tablet [Boscogen, Inc.]" (PDF). DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine. November 2010. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ^ a b "Product Information: Periactin (cyproheptadine hydrochloride)" (PDF). Aspen Pharmacare Australia. Aspen Pharmacare Australia Pty Ltd. 17 November 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 26 October 2013.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 547. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Cyproheptadine - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.