| cystathionine γ-lyase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
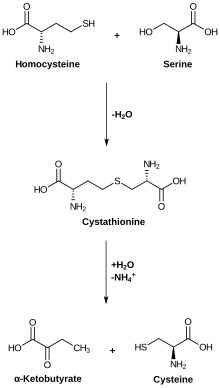 Cysteine metabolism. Cystathionase catalyzes the lower reaction. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 4.4.1.1 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9012-96-8 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| cystathionase (cystathionine γ-lyase) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | CTH | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 1491 | ||||||
| HGNC | 2501 | ||||||
| OMIM | 607657 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001902 | ||||||
| UniProt | P32929 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 4.4.1.1 | ||||||
| Locus | Chr. 1 p31.1 | ||||||
| |||||||
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:
- L-cystathionine + H2O = L-cysteine + 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (overall reaction)
- (1a) L-cystathionine = L-cysteine + 2-aminobut-2-enoate
- (1b) 2-aminobut-2-enoate = 2-iminobutanoate (spontaneous)
- (1c) 2-iminobutanoate + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (spontaneous)
Pyridoxal phosphate is a prosthetic group of this enzyme.[1][2][3]
Cystathionine γ-lyase also catalyses the following elimination reactions:
- L-homoserine to form H2O, NH3 and 2-oxobutanoate
- L-cystine, producing thiocysteine, pyruvate and NH3[4]
- L-cysteine producing pyruvate, NH3 and H2S
In some bacteria and mammals, including humans, this enzyme takes part in generating hydrogen sulfide.[2][5] Hydrogen sulfide is one of a few gases that was recently discovered to have a role in cell signaling in the body.[6]
- ^ Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2012). Biochemistry (7th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman Company.
- ^ a b Sun Q, Collins R, Huang S, Holmberg-Schiavone L, Anand GS, Tan CH, van-den-Berg S, Deng LW, Moore PK, Karlberg T, Sivaraman J (2009). "Structural basis for the inhibition mechanism of human cystathionine γ-lyase, an enzyme responsible for the production of H2S". J. Biol. Chem. 284 (5): 3076–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805459200. PMID 19019829.
- ^ Steegborn C, Clausen T, Sondermann P, Jacob U, Worbs M, Marinkovic S, Huber R, Wahl MC (1999). "Kinetics and inhibition of recombinant human cystathionine γ-lyase. Toward the rational control of transsulfuration". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (18): 12675–84. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.18.12675. PMID 10212249.
- ^ Yamanishi T, Tuboi S (1981). "The mechanism of the L-cystine cleavage reaction catalyzed by rat liver γ-cystathionase". J. Biochem. 89 (6): 1913–21. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133393. PMID 7287665.
- ^ Wang R (March 2010). "Toxic Gas, Lifesaver". Scientific American. 302 (3): 66–71. Bibcode:2010SciAm.302c..66W. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0310-66. PMID 20184185.
- ^ Wang M, Guo Z, Wang S (2013). "The effect of certain conditions in the regulation of cystathionine γ-lyase by exogenous hydrogen sulfide in mammalian cells". Biochem. Genet. 51 (7–8): 503–13. doi:10.1007/s10528-013-9581-1. PMID 23515848. S2CID 6865017.