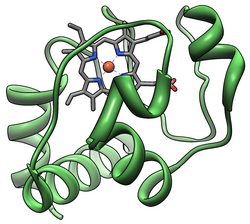
The cytochrome complex, or cyt c, is a small hemeprotein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where it plays a critical role in cellular respiration. It transfers electrons between Complexes III (Coenzyme Q – Cyt c reductase) and IV (Cyt c oxidase). Cytochrome c is highly water-soluble, unlike other cytochromes. It is capable of undergoing oxidation and reduction as its iron atom converts between the ferrous and ferric forms, but does not bind oxygen. It also plays a major role in cell apoptosis. In humans, cytochrome c is encoded by the CYCS gene.[5][6]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000172115 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000063694 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: cytochrome c".
- ^ Tafani M, Karpinich NO, Hurster KA, Pastorino JG, Schneider T, Russo MA, et al. (March 2002). "Cytochrome c release upon Fas receptor activation depends on translocation of full-length bid and the induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (12): 10073–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111350200. PMID 11790791.