| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
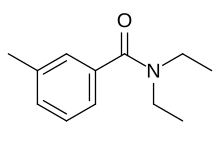
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide | |
| Other names
N,N-Diethyl-m-toluamide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.682 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H17NO | |
| Molar mass | 191.27 g/mol |
| Density | 0.998 g/mL |
| Melting point | −33 °C (−27 °F; 240 K) |
| Boiling point | 288 to 292 °C (550 to 558 °F; 561 to 565 K) |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03BX02 (WHO) QP53GX01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H315, H319, H402 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N,N-Diethyl-meta-toluamide, also called diethyltoluamide or DEET (/diːt/, from DET, the initials of di- + ethyl + toluamide),[1][2] is the oldest, one of the most effective and most common active ingredient in commercial insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection against mosquitoes, flies, ticks, fleas, chiggers, leeches, and many other biting insects.
Unlike icaridin, DEET emits an odor that many find unpleasant, leaves skin greasy, dissolves plastics and synthetic fabrics[3] and interacts negatively with sunscreen.[4][5]
- ^ "DEET". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2023-06-04.
- ^ Plumlee KH (2004-01-01), Plumlee KH (ed.), "Chapter 21 - Insecticides and Molluscicides", Clinical Veterinary Toxicology, Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 177–192, doi:10.1016/b0-32-301125-x/50024-8, ISBN 978-0-323-01125-9
- ^ "Picaridin vs DEET: Which Is the Best Insect Repellent?". Appalachian Mountain Club. 4 August 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
cdcyb2024was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
jdt2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
