| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
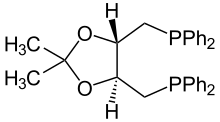
| IUPAC name
O-Isopropylidene-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane
| |
| Other names
(−)-2,3-O-Isopropylidene-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane
(−)-1,4-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,4-dideoxy-2,3-O-isopropylidene-L-threitol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C31H32O2P2 | |
| Molar mass | 498.543 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 86 to 89 °C (187 to 192 °F; 359 to 362 K) |
| Insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
DIOP (2,3-O-isopropylidene-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane) is an organophosphorus compound that is used as a chiral ligand in asymmetric catalysis. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
DIOP is prepared from the acetonide of d,l-tartaric acid, which is reduced prior to attachment of the PPh2 substituents.