
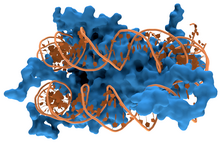


DNA-binding proteins are proteins that have DNA-binding domains and thus have a specific or general affinity for single- or double-stranded DNA.[3][4][5] Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins generally interact with the major groove of B-DNA, because it exposes more functional groups that identify a base pair.[6][7]
- ^ Created from PDB 1LMB
- ^ Created from PDB 1RVA
- ^ Travers, A. A. (1993). DNA-protein interactions. London: Springer. ISBN 978-0-412-25990-6.
- ^ Pabo CO, Sauer RT (1984). "Protein-DNA recognition". Annu. Rev. Biochem. 53 (1): 293–321. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. PMID 6236744.
- ^ Dickerson R.E. (1983). "The DNA helix and how it is read". Sci Am. 249 (6): 94–111. Bibcode:1983SciAm.249f..94D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1283-94.
- ^ Zimmer C, Wähnert U (1986). "Nonintercalating DNA-binding ligands: specificity of the interaction and their use as tools in biophysical, biochemical and biological investigations of the genetic material". Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 47 (1): 31–112. doi:10.1016/0079-6107(86)90005-2. PMID 2422697.
- ^ Dervan PB (April 1986). "Design of sequence-specific DNA-binding molecules". Science. 232 (4749): 464–71. Bibcode:1986Sci...232..464D. doi:10.1126/science.2421408. PMID 2421408.