Danelaw | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 886–1066[1] | |||||||||
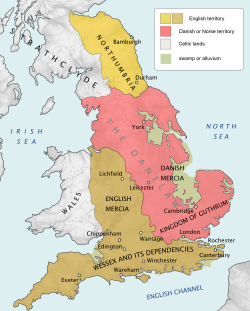 England, 886 | |||||||||
| Common languages | Old Norse Old English | ||||||||
| Religion | Christianity | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 886 | |||||||||
| 1066[1] | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | England | ||||||||
The Danelaw (/ˈdeɪnˌlɔː/, Danish: Danelagen; Norwegian: Danelagen; Old English: Dena lagu)[2] was the part of England between the early tenth century and the Norman Conquest under Anglo-Saxon rule in which Danish laws applied.[3] The Danelaw originated in the conquest and occupation of large parts of eastern and northern England by Danish Vikings in the late ninth century. The term applies to the areas in which English kings allowed the Danes to keep their own laws following the tenth-century English conquest in return for the Danish settlers' loyalty to the English crown. "Danelaw" is first recorded in the early 11th century as Dena lage.[4]
The Danelaw originated from the invasion of the Great Heathen Army into England in 865, but the term was not used to describe a geographic area until the 11th century. With the increase in population and productivity in Scandinavia, Viking warriors, having sought treasure and glory in the nearby British Isles, "proceeded to plough and support themselves", in the words of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle for 876.[5]
Danelaw can describe the set of legal terms and definitions created in the treaties between Alfred the Great, the king of Wessex, and Guthrum, the Danish warlord, written following Guthrum's defeat at the Battle of Edington in 878.
In 886, the Treaty of Alfred and Guthrum was formalised, defining the boundaries of their kingdoms, with provisions for peaceful relations between the English and the Vikings. The language spoken in England was affected by this clash of cultures, with the emergence of Anglo-Norse dialects.[6]
The Danelaw roughly comprised these contemporary 16 ceremonial counties and shires: Greater London, Leicester, York, Nottingham, Derby, Lincoln, Essex, Cambridge, Suffolk, Norfolk, Northampton, Huntingdon, Bedford, Hertford, Middlesex, and Buckingham.[7][8][9]
- ^ Higham, Nicholas (2014). "Danelaw". In Lapidge, Michael; Blair, John; Keynes, Simon; Scragg, Donald (eds.). The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Anglo-Saxon England (2nd ed.). Chichester, West Sussex: Wiley Blackwell. pp. 139–140. ISBN 978-0-470-65632-7.
- ^ M. Pons-Sanz (2007). Norse-derived Vocabulary in late Old English Texts: Wulfstan's Works. A Case Study. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 71. ISBN 978-87-7674-196-9.
- ^ "The Old English word Dene ("Danes") usually refers to Scandinavians of any kind; most of the invaders were indeed Danish (East Norse speakers), but there were Norwegians (West Norse [speakers]) among them as well." Lass, Roger, Old English: A Historical Linguistic Companion, p. 187, n. 12. Cambridge University Press, 1994.
- ^ Abrams, Lesley (2001). "Edward the Elder's Danelaw". In Higham, N. J.; Hill, D. H. (eds.). Edward the Elder 899–924. Abingdon, UK: Routledge. p. 128. ISBN 0-415-21497-1.
- ^ Quoted by Richard Hall, Viking Age Archaeology (series Shire Archaeology), 2010:22; Gwyn Jones, A History of the Vikings. Revised ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1984: 221.
- ^ "Danelaw Heritage". The Viking Network. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ S. Thomason, T. Kaufman, Language Contact, Creolisation and Genetic Linguistics, (1988) p. 362
- ^ K. Holman, The Northern Conquest: Vikings in Britain and Ireland, (2007) p. 157
- ^ The Blackwell Encyclopedia of Anglo-Saxon England, ed. Michael Lapidge (2008), p. 136