
In propositional logic and Boolean algebra, De Morgan's laws,[1][2][3] also known as De Morgan's theorem,[4] are a pair of transformation rules that are both valid rules of inference. They are named after Augustus De Morgan, a 19th-century British mathematician. The rules allow the expression of conjunctions and disjunctions purely in terms of each other via negation.
The rules can be expressed in English as:
- The negation of "A and B" is the same as "not A or not B".
- The negation of "A or B" is the same as "not A and not B".
or
- The complement of the union of two sets is the same as the intersection of their complements
- The complement of the intersection of two sets is the same as the union of their complements
or
- not (A or B) = (not A) and (not B)
- not (A and B) = (not A) or (not B)
where "A or B" is an "inclusive or" meaning at least one of A or B rather than an "exclusive or" that means exactly one of A or B.

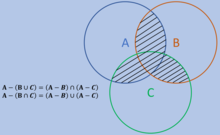
Another form of De Morgan's law is the following as seen below.
Applications of the rules include simplification of logical expressions in computer programs and digital circuit designs. De Morgan's laws are an example of a more general concept of mathematical duality.
- ^ Copi, Irving M.; Cohen, Carl; McMahon, Kenneth (2016). Introduction to Logic. doi:10.4324/9781315510897. ISBN 9781315510880.
- ^ Hurley, Patrick J. (2015), A Concise Introduction to Logic (12th ed.), Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-1-285-19654-1
- ^ Moore, Brooke Noel (2012). Critical thinking. Richard Parker (10th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-803828-0. OCLC 689858599.
- ^ DeMorgan's [sic] Theorem
- ^ Kashef, Arman. (2023), In Quest of Univeral Logic: A brief overview of formal logic's evolution, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.24043.82724/1

