 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
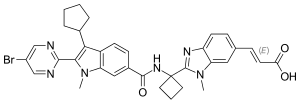
| Formula | C34H33BrN6O3 |
| Molar mass | 653.581 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Deleobuvir (formerly BI 207127) was an experimental drug for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was being developed by Boehringer Ingelheim. It is a non-nucleoside hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor. Deleobuvir was tested in combination regimens with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, and in interferon-free regimens with other direct-acting antiviral agents including faldaprevir.[citation needed]
Data from the SOUND-C2 study, presented at the 2012 AASLD Liver Meeting, showed that a triple combination of deleobuvir, faldaprevir, and ribavirin performed well in HCV genotype 1b patients.[1] Efficacy fell below 50%, however, for dual regimens without ribavirin and for genotype 1a patients.[citation needed]
These results were confirmed in the SOUND-C3 study, presented at the 2013 APASL Liver Conference, which found that 16-week triple therapy with deleobuvir + faldaprevir + ribavirin gave 95% SVR12 in HCV genotype 1b patients but poor virological response in genotype 1a.[2]
In December 2013, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that the development of deleobuvir would not be continued since recent findings from phase III trials did not suggest sufficient efficacy.[citation needed]
- ^ Interferon-free hepatitis C treatment with faldaprevir proves safe and effective in people with cirrhosis. Alcorn, K. Aidsmap.com. 20 November 2012.
- ^ Dufour JF, Buti M, Soriano V, Buy-nak R, Mantry P, Taunk J, et al. Interferon-free treatment with faldaprevir, deleobuvir (BI 207127) and ribavirin in SOUND-C3: 95% SVR12 in HCV GT-1b. 23rd Conference of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) 6–9 June 2013. Retrieved 12 Sep 2013.