| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Monoceros |
| Right ascension | 07h 11m 51.860s[1] |
| Declination | −00° 29′ 33.96″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.15[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A2V[3] or A0IV[4] |
| U−B color index | +0.04[5] |
| B−V color index | +0.00[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +15.0±4.1[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +0.79[7] mas/yr Dec.: +4.52[7] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 8.49 ± 0.17 mas[7] |
| Distance | 384 ± 8 ly (118 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.20[2] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.4+0.43 −0.38[3] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 350[8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.5±0.25[3] cgs |
| Temperature | 9,462[8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.00[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 175.5±1.3[10] km/s |
| Age | 405+135 −207[3] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
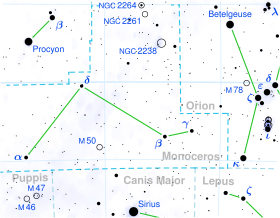
Delta Monocerotis, which is Latinized from δ Monocerotis, is a single star[12] in the constellation of Monoceros, positioned about a half degree south of the celestial equator. It has a white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.15.[2] The distance to this star is approximately 384 light years based on parallax.[7] It is drifting further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of about +15 km/s,[6] having come to within 88 light-years some 7.3 million years ago.[2] The star has an absolute magnitude of −1.20.[2]
The Bright Star Catalogue assigns this star a stellar classification of A2V, suggesting this is an A-type main-sequence star.[3][13] However, Houk and Swift (1999) found a more evolved subgiant class of A0IV.[4] It has around 2.4 times the mass of the Sun and is an estimated 405 million years old.[3] The star has a high rate of spin with a projected rotational velocity of 175.5 km/s,[10] giving it an equatorial bulge that is 5% larger than the polar radius.[14] It is radiating 350 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 9,462 K.[8]
It has one reported visual companion, designated component B, at an angular separation of 32.0″ and visual magnitude 13.0.[15]
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Høg2000was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
XHIPwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
Gullikson2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Houk1999was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Mallama2014was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Gontcharov2006was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
vanLeeuwen2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Zorec2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Gontcharov2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Díaz2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Eggleton2008was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hoffleit1991was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
vanBelle2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
CCDMwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).