| Dermatofibroma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Dermal dendrocytoma,[1] Dermatofibroma,[2] Fibrous dermatofibroma,[2] Fibrous histiocytoma,[2] Fibroma simplex,[1] Nodular subepidermal fibrosis,[1] and Sclerosing hemangioma[1]) |
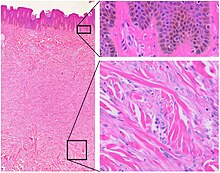 | |
| Histopathology of dermatofibroma, with basilar hyperpigmentation of the overlying epidermis (top right), and spindled fibroblasts with collagen entrapment. HE stain. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
A dermatofibroma, or benign fibrous histiocytomas, is a benign nodule in the skin, typically on the legs, elbows or chest of an adult.[3] It is usually painless.[3]
It usually ranges from 0.2cm to 2cm in size but larger examples have been reported.[3] It typically results from mild trauma such as an insect bite.[3] Risk factors for developing multiple dermatofibromas include lupus, HIV, blood cancer and some medicines that weaken immunity.[3]
It is usually diagnosed by its appearance, but a biopsy may be required.[3] Other bumps such as granular cell tumor, melanoma, clear cell acanthoma and dermatofibrosis lenticularis disseminata may look similar.[3] Usually no treatment is needed.[3] It can remain unchanged for years but can resolve spontaneously.[3]
- ^ a b c d Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.[page needed]
- ^ a b c Freedberg; et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 668. ISBN 978-0-07-138076-8.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "28. Dermal and subcutaneous tumors". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 617–618. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6.