 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | des-FLOO-rane |
| Trade names | Suprane |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Not metabolized |
| Elimination half-life | Elimination dependent on minute ventilation |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.214.382 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
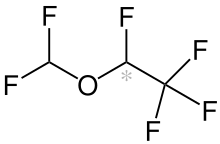
| Formula | C3H2F6O |
| Molar mass | 168.038 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Desflurane (1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a highly fluorinated methyl ethyl ether used for maintenance of general anesthesia. Like halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, it is a racemic mixture of (R) and (S) optical isomers (enantiomers). Together with sevoflurane, it is gradually replacing isoflurane for human use, except in economically undeveloped areas, where its high cost precludes its use. It has the most rapid onset and offset of the volatile anesthetic drugs used for general anesthesia due to its low solubility in blood.
Some drawbacks of desflurane are its low potency, its pungency and its high cost (though at low flow fresh gas rates, the cost difference between desflurane and isoflurane appears to be insignificant[2]). It may cause tachycardia and airway irritability when administered at concentrations greater than 10% by volume. Due to this airway irritability, desflurane is infrequently used to induce anesthesia via inhalation techniques.
Though it vaporizes very readily, it is a liquid at room temperature. Anaesthetic machines are fitted with a specialized anaesthetic vaporiser unit that heats liquid desflurane to a constant temperature. This enables the agent to be available at a constant vapor pressure, negating the effects fluctuating ambient temperatures would otherwise have on its concentration imparted into the fresh gas flow of the anesthesia machine.
Desflurane, along with enflurane and to a lesser extent isoflurane, has been shown to react with the carbon dioxide absorbent in anesthesia circuits to produce detectable levels of carbon monoxide through degradation of the anesthetic agent. The CO2 absorbent Baralyme, when dried, is most culpable for the production of carbon monoxide from desflurane degradation, although it is also seen with soda lime absorbent as well. Dry conditions in the carbon dioxide absorbent are conducive to this phenomenon, such as those resulting from high fresh gas flows.[3]
- ^ Anvisa (31 March 2023). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 4 April 2023). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ Varkey JK (October 2012). Cost Analysis of Desflurane and Sevoflurane: An Integrative Review and Implementation Project Introducing the Volatile Anesthetic Cost Calculator (Doctor of Nursing Practice thesis). Texas Christian University.
- ^ Fang ZX, Eger EI, Laster MJ, Chortkoff BS, Kandel L, Ionescu P (June 1995). "Carbon monoxide production from degradation of desflurane, enflurane, isoflurane, halothane, and sevoflurane by soda lime and Baralyme". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 80 (6): 1187–93. doi:10.1097/00000539-199506000-00021. PMID 7762850. S2CID 41150462.