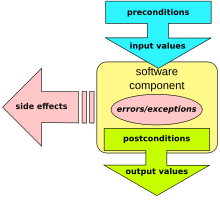
Design by contract (DbC), also known as contract programming, programming by contract and design-by-contract programming, is an approach for designing software.
It prescribes that software designers should define formal, precise and verifiable interface specifications for software components, which extend the ordinary definition of abstract data types with preconditions, postconditions and invariants. These specifications are referred to as "contracts", in accordance with a conceptual metaphor with the conditions and obligations of business contracts.
The DbC approach assumes all client components that invoke an operation on a server component will meet the preconditions specified as required for that operation.
Where this assumption is considered too risky (as in multi-channel or distributed computing), the inverse approach is taken, meaning that the server component tests that all relevant preconditions hold true (before, or while, processing the client component's request) and replies with a suitable error message if not.