| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
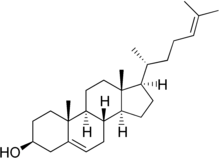
| IUPAC name
Cholesta-5,24-dien-3β-ol
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bS,7S,9aR,9bS,11aR)-9a,11a-Dimethyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylhept-5-en-2-yl]-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.671 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H44O | |
| Molar mass | 384.64 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 121.5 °C (250.7 °F; 394.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Desmosterol (Cholesta-5,24-dien-3β-ol) is a lipid present in the membrane of phytoplankton and an intermediate product in cholesterol synthesis in mammal cells.[1] Structurally, desmosterol has a similar backbone to cholesterol, with the exception of an additional double bond in the structure of desmosterol.
The similarity can be seen biologically through the synthesis of cholesterol in the human body, as desmosterol is the immediate precursor to cholesterol in the Bloch pathway.[2] Desmosterol is accumulated in desmosterolosis and undergoes reduction with the catalyst 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase to form cholesterol.[3]
In 2014, desmosterol was named the Molecule of the Year 2012 by the International Society for Molecular and Cell Biology and Biotechnology Protocols and Researches (ISMCBBPR).[4]

- ^ Kamal, Md. Arif; Pal, Antara (September 2023). "Effect of Desmosterol, Lathosterol and Coprostanol on the phase behaviour of phospholipid membranes". Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. 673: 131489. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.131489.
- ^ Bloch, Konrad (October 1965). "The Biological Synthesis of Cholesterol". Science. 150 (3692): 19–28. Bibcode:1965Sci...150...19B. doi:10.1126/science.150.3692.19. PMID 5319508.
- ^ Keber, Rok; Rozman, Damjana; Horvat, Simon (January 2013). "Sterols in spermatogenesis and sperm maturation". Journal of Lipid Research. 54 (1): 20–33. doi:10.1194/jlr.R032326. PMC 3520525. PMID 23093550.
- ^ "Announcing ISMCBBPR's Molecule of the Year 2012". Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2014-02-22.