 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Permonid |
| Other names | Desomorphine, krokodil, dihydrodesoxymorphine, Permonid |
| Addiction liability | Very High |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.406 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
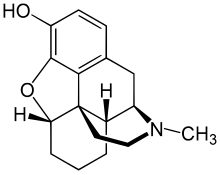
| Formula | C17H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 271.360 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Desomorphine[note 1] is a semi-synthetic opioid commercialized by Roche, with powerful, fast-acting effects, such as sedation and analgesia.[3][4][5][6] It was first discovered and patented in Germany by a German team working for Knoll in 1920[7] but was not generally recognized. It was later synthesized in 1932 by American chemist Lyndon Frederick Small. Small also successfully patented it in 1934 in the United States.[8] Desomorphine was used in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland under the brand name Permonid[9] and was described as having a fast onset and a short duration of action, with relatively little nausea compared to equivalent doses of morphine. Dose for dose it is roughly ten times more potent than morphine, with 1 mg desomorphine being equivalent 10 mg morphine, via the intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) routes.[10]
Desomorphine is a morphine analogue where the 6-hydroxyl group and the 7,8 double bond have been reduced.[8] The traditional synthesis of desomorphine starts from α-chlorocodide, which is itself obtained by treating codeine with thionyl chloride. By catalytic reduction, α-chlorocodide gives dihydrodesoxycodeine, which yields desomorphine on demethylation.[11][12]
A desomorphine product, usually based on codeine, has been developed as a recreational drug.[13] The product in question is typically a highly impure variant of desomorphine. The scaly sores and necrosis that develop around the injection site has prompted the name krokodil (Russian for crocodile).
- ^ Shuster S (5 December 2013). "The World's Deadliest Drug: Inside a Krokodil Cookhouse". Time.
- ^ Christensen J (18 October 2013). "Flesh-eating 'zombie' drug 'kills you from the inside out'". CNN.
- ^ Casy AF, Parfitt RT (1986). Opioid analgesics: chemistry and receptors. New York: Plenum Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-306-42130-3.
- ^ Bognar R, Makleit S (June 1958). "Neue Methode für die Vorbereitung von dihydro-6-desoxymorphine" [New method for the preparation of dihydro-6-desoxymorphine]. Arzneimittel-Forschung (in German). 8 (6): 323–5. PMID 13546093.
- ^ Janssen PA (April 1962). "A Review of the Chemical Features Associated with Strong Morphine-Like Activity". British Journal of Anaesthesia. 34 (4): 260–8. doi:10.1093/bja/34.4.260. PMID 14451235.
- ^ Sargent LJ, May EL (November 1970). "Agonists--antagonists derived from desomorphine and metopon". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (6): 1061–3. doi:10.1021/jm00300a009. PMID 4098039.
- ^ DE Patent 414598C 'Verfahren zur Herstellung von Dihydrodesoxymorphin und Dihydrodesoxycodein'
- ^ a b US patent 1980972, Lyndon Frederick Small, "Morphine Derivative and Processes", published 1934-19-07, issued 1934-13-11
- ^ "Krokodil". New York State Office of Alcoholism and Substance Abuse Services. Archived from the original on 13 February 2014. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
lifsciwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Mosettig E, Cohen FL, Small LF (1932). "Desoxycodeine Studies. III. The Constitution of the So-Called α-Dihydrodesoxycodeine: Bis-Dihydrodesoxycodeine". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 54 (2): 793–801. doi:10.1021/ja01341a051.
- ^ Eddy NB, Howes HA (1935). "Studies of Morphine, Codeine and their Derivatives X. Desoxymorphine-C, Desoxycodeine-C and their Hydrogenated Derivatives". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 55 (3): 257–67.
- ^ Alves EA (December 2020). "DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Krokodil". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 11 (23): 3968–3978. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00495. PMID 32877160. S2CID 221476977.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).