 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Austedo |
| Other names | Tetrabenazine D6; SD809; SD-809 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a617022 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
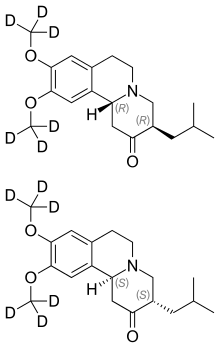
| Formula | C19H21D6NO3 |
| Molar mass | 323.462 g·mol−1 |
Deutetrabenazine (trade name Austedo) is a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitor which is used for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease and tardive dyskinesia.
Chemically, deutetrabenazine is an isotopic isomer of tetrabenazine in which six hydrogen atoms have been replaced by deuterium atoms. The incorporation of deuterium slows the rate of drug metabolism, allowing less frequent dosing.[5][6]
- ^ a b "Austedo". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 9 June 2021. Archived from the original on 6 September 2021. Retrieved 6 September 2021.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "AusPAR: Deutetrabenazine". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 27 May 2022. Archived from the original on 27 May 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ Anvisa (31 March 2023). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 4 April 2023). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ Citrome L (April 2016). "Breakthrough drugs for the interface between psychiatry and neurology". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 70 (4): 298–299. doi:10.1111/ijcp.12805. PMID 27028671. Archived from the original on 21 August 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2017.
- ^ Coppen EM, Roos RA (January 2017). "Current Pharmacological Approaches to Reduce Chorea in Huntington's Disease". Drugs. 77 (1): 29–46. doi:10.1007/s40265-016-0670-4. PMC 5216093. PMID 27988871.