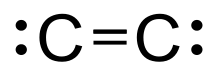
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diatomic carbon
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethenediylidene (substitutive) Dicarbon(C—C) (additive) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 196 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2 | |
| Molar mass | 24.022 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diatomic carbon (systematically named dicarbon and 1λ2,2λ2-ethene), is a green, gaseous inorganic chemical with the chemical formula C=C (also written [C2] or C2). It is kinetically unstable at ambient temperature and pressure, being removed through autopolymerisation. It occurs in carbon vapor, for example in electric arcs; in comets, stellar atmospheres, and the interstellar medium; and in blue hydrocarbon flames.[1] Diatomic carbon is the second simplest of the allotropes of carbon (after atomic carbon), and is an intermediate participant in the genesis of fullerenes.
- ^ Hoffmann, Roald (1995). "Marginalia: C2 In All Its Guises" (PDF). American Scientist. 83 (4): 309–311. Bibcode:1995AmSci..83..309H. JSTOR 29775475. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-03-21. Retrieved 2017-07-22.