
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dibenzo[b,d]furan | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 121100 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.612 |
| EC Number |
|
| 67825 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8O | |
| Molar mass | 168.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 81 to 85 °C (178 to 185 °F; 354 to 358 K) |
| Boiling point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332, H411 | |
| P273, P391, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Furan Benzofuran Dibenzodioxin Dibenzothiophene Carbazole Polyozellin (compound with a kernel with two dibenzofurans that share the same benzene ring) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
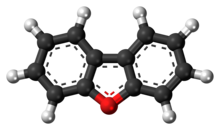
Dibenzofuran is a heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical structure shown at right. It is an aromatic compound that has two benzene rings fused to a central furan ring. All the numbered carbon atoms have a hydrogen atom bonded to each of them. It is a volatile white solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is obtained from coal tar, where it exists as a 1% component.[1]
- ^ Gerd Collin and Hartmut Höke "Benzofurans" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.l03_l01