| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
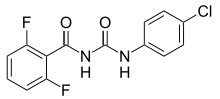
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbamoyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide | |
| Other names
Dimilin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.740 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C14H9ClF2N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 310.68 g·mol−1 |
| 0.08 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | DMSO: 12 g/100 g Acetone 0.615 g/100 g Methanol: 0.09 g/100 g |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP53BC02 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Diflubenzuron is an insecticide of the benzoylurea class.[2] It is used in forest management and on field crops[3] to selectively control insect pests, particularly forest tent caterpillar moths, boll weevils, gypsy moths, and other types of moths.[1] It is a widely used larvicide in India for control of mosquito larvae by public health authorities. Diflubenzuron is approved by the WHO Pesticide Evaluation Scheme.[1]
- ^ a b c Diflubenzuron Pesticide Information Profile, Extension Toxicology Network
- ^ Junquera, Pablo; Hosking, Barry; Gameiro, Marta; Macdonald, Alicia (2019). "Benzoylphenyl ureas as veterinary antiparasitics. An overview and outlook with emphasis on efficacy, usage and resistance". Parasite. 26: 26. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019026. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 6492539. PMID 31041897.

- ^ Johnson, Douglas (2016). "Insecticide Recommendations for Soybeans - 2016" (PDF). Cooperative Extension Service. University of Kentucky: College of Agriculture, Food and Environment. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 16 February 2016.