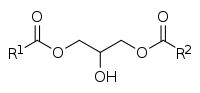
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages.[1] Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides.[2] DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat;[3][4] with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.[3]
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "glycerides". doi:10.1351/goldbook.G02647
- ^ "Toxicological evaluation of some food additives including anticaking agents, antimicrobials, antioxidants, emulsifiers and thickening agents". World Health Organization.
- ^ a b Phuah, Eng-Tong; Tang, Teck-Kim; Lee, Yee-Ying; et al. (2015). "Review on the Current State of Diacylglycerol Production Using Enzymatic Approach" (PDF). Food and Bioprocess Technology. 8 (6): 1169–1186. doi:10.1007/s11947-015-1505-0. ISSN 1935-5130. S2CID 84353775.
- ^ Lo, Seong-Koon; Tan, Chin-Ping; Long, Kamariah; et al. (2008). "Diacylglycerol Oil—Properties, Processes and Products: A Review" (PDF). Food and Bioprocess Technology. 1 (3): 223–233. doi:10.1007/s11947-007-0049-3. ISSN 1935-5130. S2CID 86604260.