In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups (−OH) are substituted onto a benzene ring (C6H6). These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene (the ortho isomer) is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene (the meta isomer) is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene (the para isomer) is commonly known as hydroquinone.[1]
Isomer ortho meta para Trivial name Catechol Resorcinol Hydroquinone IUPAC name benzene-1,2-diol benzene-1,3-diol benzene-1,4-diol Other names pyrocatechol
1,2-dihydroxybenzene
o-dihydroxybenzene
o-benzenediolresorcin
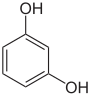
1,3-dihydroxybenzene
m-dihydroxybenzene
m-benzenediol1,4-dihydroxybenzene
p-dihydroxybenzene
p-benzenediolStructure 

All three of these compounds are colorless to white granular solids at room temperature and pressure, but upon exposure to oxygen they may darken. All three isomers have the chemical formula C6H6O2.
Similar to other phenols, the hydroxyl groups on the aromatic ring of a benzenediol are weakly acidic. Each benzenediol can lose an H+ from one of the hydroxyls to form a type of phenolate ion.
The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (−CH=O) or ketone (>C=O) reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group (C=O) is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
- ^ Helmut Fiege; Heinz-Werner Voges; Toshikazu Hamamoto; Sumio Umemura; Tadao Iwata; Hisaya Miki; Yasuhiro Fujita; Hans-Josef Buysch; Dorothea Garbe; Wilfried Paulus (2002). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.

