| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dioxygenyl
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
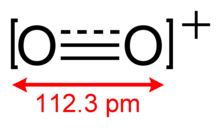
The dioxygenyl ion, O+
2, is a rarely-encountered oxycation in which both oxygen atoms have a formal oxidation state of +1/2. It is formally derived from oxygen by the removal of an electron:
- O2 → O+
2 + e−
The energy change for this process is called the ionization energy of the oxygen molecule. Relative to most molecules, this ionization energy is very high at 1175 kJ/mol.[1] As a result, the scope of the chemistry of O+
2 is quite limited, acting mainly as a 1-electron oxidiser.[2]
- ^ Michael Clugston; Rosalind Flemming (2000). Advanced Chemistry, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-914633-0, ISBN 978-0-19-914633-8, p. 355.
- ^ Foote, Christopher S.; Valentine, Joan S. (1995). Active oxygen in chemistry. Joel F. Liebman, A. Greenberg. Springer. ISBN 0-412-03441-7.