| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Disulfur dichloride
Dichlorodisulfane | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Chlorosulfanyl thiohypochlorite | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.021 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | Sulfur+monochloride | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 3390 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| S2Cl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 135.02 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Light-amber to yellow-red, oily liquid[1] | ||
| Odor | pungent, nauseating, irritating[1] | ||
| Density | 1.688 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −80 °C (−112 °F; 193 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 137.1 °C (278.8 °F; 410.2 K) | ||
| Decomposes, with loss of HCl | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, benzene, ether, THF, chloroform, CCl4[2] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 7 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
| −62.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.658 | ||
| Structure | |||
| C2 | |||
| 2 at sulfur atoms | |||
| gauche | |||
| 1.60 D[2] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H314, H332, H400 | |||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 118.5 °C (245.3 °F; 391.6 K) | ||
| 234 °C (453 °F; 507 K) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
150 ppm (mouse, 1 min) (1 ppm = 5.52 mg/m3)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 ppm (5.52 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
C 1 ppm (5.52 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
5 ppm[1] (1 ppm = 5.52 mg/m3) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0958 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related sulfur chlorides/oxychlorides
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Disulfur dichloride (or disulphur dichloride by the British English spelling) is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2.[4][5][6][7] It is an amber oily liquid.
Sometimes, this compound is incorrectly named sulfur monochloride (or sulphur monochloride by the British English spelling), the name implied by its empirical formula SCl.
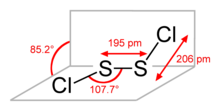
S2Cl2 has the structure implied by the formula Cl−S−S−Cl, wherein the dihedral angle between the Cla−S−S and S−S−Clb planes is 85.2°. This structure is referred to as gauche, and is akin to that for H2O2. A rare isomer of S2Cl2 is S=SCl2 (thiothionyl chloride); this isomer forms transiently when S2Cl2 is exposed to UV-radiation (see thiosulfoxides).
- ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0578". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ^ "Sulfur monochloride". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. Inorganic Chemistry Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Hartman, W. W.; Smith, L. A.; Dickey, J. B. (1934). "Diphenylsulfide". Organic Syntheses. 14: 36; Collected Volumes, vol. 2, p. 242.
- ^ R. J. Cremlyn An Introduction to Organosulfur Chemistry John Wiley and Sons: Chichester (1996). ISBN 0-471-95512-4
- ^ Garcia-Valverde M., Torroba T. (2006). "Heterocyclic chemistry of sulfur chlorides – Fast ways to complex heterocycles". European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2006 (4): 849–861. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200500786.


