| Dugong Temporal range: Miocene–recent[1]
| |
|---|---|

| |
| A dugong photographed underwater | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Sirenia |
| Family: | Dugongidae |
| Subfamily: | Dugonginae |
| Genus: | Dugong Lacépède, 1799[4] |
| Species: | D. dugon
|
| Binomial name | |
| Dugong dugon (Müller, 1776)
| |
| |
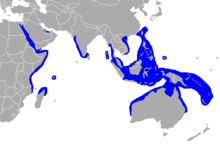
| Dugong range | |
The dugong (/ˈd(j)uːɡɒŋ/; Dugong dugon) is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest modern relative, Steller's sea cow (Hydrodamalis gigas), was hunted to extinction in the 18th century.
The dugong is the only sirenian in its range, which spans the waters of some 40 countries and territories throughout the Indo-West Pacific. The dugong is largely dependent on seagrass communities for subsistence and is thus restricted to the coastal habitats that support seagrass meadows, with the largest dugong concentrations typically occurring in wide, shallow, protected areas such as bays, mangrove channels, the waters of large inshore islands and inter-reefal waters. The northern waters of Australia between Shark Bay and Moreton Bay are believed to be the dugong's contemporary stronghold.
Like all modern sirenians, the dugong has a fusiform body with no dorsal fin or hind limbs. The forelimbs or flippers are paddle-like. The dugong is easily distinguishable from the manatees by its fluked, dolphin-like tail; moreover, it possesses a unique skull and teeth. Its snout is sharply downturned, an adaptation for feeding in benthic seagrass communities. The molar teeth are simple and peg-like, unlike the more elaborate molar dentition of manatees.
The dugong has been hunted for thousands of years for its meat and oil. Traditional hunting still has great cultural significance in several countries in its modern range, particularly northern Australia and the Pacific Islands. The dugong's current distribution is fragmented, and many populations are believed to be close to extinction. The IUCN lists the dugong as a species vulnerable to extinction, while the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species limits or bans the trade of derived products. Despite being legally protected in many countries, the main causes of population decline remain anthropogenic and include fishing-related fatalities, habitat degradation, and hunting. With its long lifespan of 70 years or more and slow rate of reproduction, the dugong is especially vulnerable to extinction.
- ^ "Dugong". www.fossilworks.org. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ Lin, Mingli; Turvey, Samuel T.; Han, Chouting; Huang, Xiaoyu; Mazaris, Antonios D.; Liu, Mingming; Ma, Heidi; Yang, Zixin; Tang, Xiaoming (24 August 2022). "Functional extinction of dugongs in China". Royal Society Open Science. 9 (8): 211994. Bibcode:2022RSOS....911994L. doi:10.1098/rsos.211994. PMC 9399689. PMID 36016916.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Archived from the original on 3 February 2007. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Shoshani, J. (2005). "Order Sirenia". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
