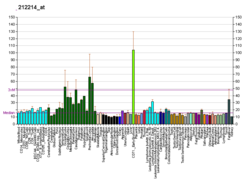
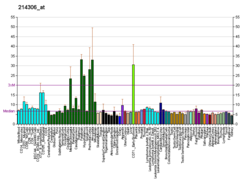
Dynamin-like 120 kDa protein, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OPA1 gene.[5][6] This protein regulates mitochondrial fusion and cristae structure in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and contributes to ATP synthesis and apoptosis,[7][8][9] and small, round mitochondria.[10] Mutations in this gene have been implicated in dominant optic atrophy (DOA), leading to loss in vision, hearing, muscle contraction, and related dysfunctions.[6][7][11]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000198836 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038084 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Votruba M, Moore AT, Bhattacharya SS (Jan 1998). "Demonstration of a founder effect and fine mapping of dominant optic atrophy locus on 3q28-qter by linkage disequilibrium method: a study of 38 British Isles pedigrees". Human Genetics. 102 (1): 79–86. doi:10.1007/s004390050657. PMID 9490303. S2CID 26060748.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: OPA1 optic atrophy 1 (autosomal dominant)".
- ^ a b Santarelli R, Rossi R, Scimemi P, Cama E, Valentino ML, La Morgia C, Caporali L, Liguori R, Magnavita V, Monteleone A, Biscaro A, Arslan E, Carelli V (Mar 2015). "OPA1-related auditory neuropathy: site of lesion and outcome of cochlear implantation". Brain. 138 (Pt 3): 563–76. doi:10.1093/brain/awu378. PMC 4339771. PMID 25564500.
- ^ Patten DA, Wong J, Khacho M, Soubannier V, Mailloux RJ, Pilon-Larose K, MacLaurin JG, Park DS, McBride HM, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Harper ME, Germain M, Slack RS (Nov 2014). "OPA1-dependent cristae modulation is essential for cellular adaptation to metabolic demand". The EMBO Journal. 33 (22): 2676–91. doi:10.15252/embj.201488349. PMC 4282575. PMID 25298396.
- ^ Anand R, Wai T, Baker MJ, Kladt N, Schauss AC, Rugarli E, Langer T (Mar 2014). "The i-AAA protease YME1L and OMA1 cleave OPA1 to balance mitochondrial fusion and fission". The Journal of Cell Biology. 204 (6): 919–29. doi:10.1083/jcb.201308006. PMC 3998800. PMID 24616225.
- ^ Wiemerslage L, Lee D (2016). "Quantification of mitochondrial morphology in neurites of dopaminergic neurons using multiple parameters". J Neurosci Methods. 262: 56–65. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.01.008. PMC 4775301. PMID 26777473.
- ^ Carelli V, Musumeci O, Caporali L, Zanna C, La Morgia C, Del Dotto V, Porcelli AM, Rugolo M, Valentino ML, Iommarini L, Maresca A, Barboni P, Carbonelli M, Trombetta C, Valente EM, Patergnani S, Giorgi C, Pinton P, Rizzo G, Tonon C, Lodi R, Avoni P, Liguori R, Baruzzi A, Toscano A, Zeviani M (Mar 2015). "Syndromic parkinsonism and dementia associated with OPA1 missense mutations". Annals of Neurology. 78 (1): 21–38. doi:10.1002/ana.24410. PMC 5008165. PMID 25820230.